 |
||
Presentation > Activities > Training > Projet OMD2

Cloud Multidisciplinary Optimizations
http://omd2.scilab.org/
![]()
October 2012
Major Advances in Cloud Multidisciplinary Optimizations
The OMD2 project has successfully developed an Open Multidisciplinary Optimization Platform for distributed and Cloud computing.
The OMD2 project has created a collaborative design platform that works in general HPC and Cloud distributed environments. The developments rely on the ProActive Parallel Suite Cloud middleware developed by ActiveEon in Open Source, and allow the users to interact directly with the Cloud platform from the SCILAB language. The developments have been validated on important car industry test cases related to car environmental impacts.
The OMD2 project prepares the French design community to the coming of the CLOUD HPC age, i.e., simulating, testing and optimizing on large parallel computer infrastructures. It creates links between the French engineering design community and more advanced communities in HPC like bioinformatics and climatology by sharing middleware and computing environments.
Applications to the OMD2 industrial test cases (the 2D and 3D shape optimization of an air duct, cf. Fig.1) have been performed thanks to the access to ProActive PACA Grid (1 400 cores), and the simulation workflows through web services put together and used by other partners of the project (Renault, CD-adapco, SIREHNA-DCNS, ACTIVEEON, INRIA, ENSM-SE, UTC, ECP, IRCCyN, ENS CACHAN, Scilab Digiteo). Below are examples of recent strong advances on test case studies realized by Ecole des Mines de Saint-Etienne:
Robust optimization
An algorithm is proposed that simultaneously estimates the average of a performance function and minimizes it. The two tasks, that of propagating uncertainties and that of optimizing, are performed in an optimal way (minimizing the estimate variance and maximizing an expected improvement), which reduces substantially the number of calls to the expensive numerical simulations.
Parallel optimization
During the OMD2 project, it has been proposed to generate sets of candidate optimal points from Gaussian processes conditioned to approximate expensive numerical simulations. The associated optimization criterion was called asynchronous multi-points expected improvement. Because the sets are made of many points, the method defines a parallel algorithm. Many implementations of such an algorithm are possible, which define various compromises between a reduced number of expensive simulations and wall-clock time reduction through the use of a large number of nodes. Thanks to the Scilab connector to the ProActive Cloud Scheduler (e.g., PAsolve, PAtask primitives), we have been able to prototype these algorithms and test them massively on the PACA grid with up to 500 tasks running in parallel (cf. Fig.2).
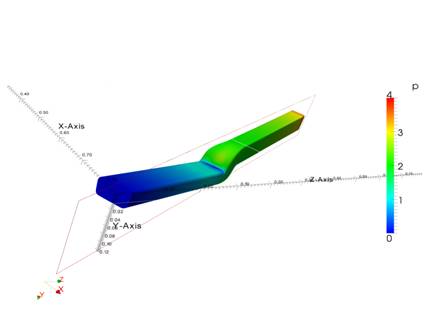
1 - Optimized shape of an air-cooling duct.
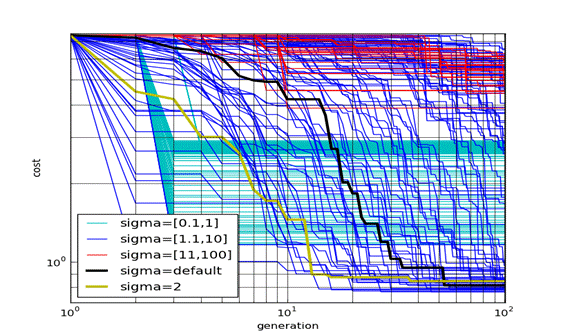
Figure 2 Massive testing of a parallel optimization on ProActive PACA Grid
Massive testing of a parallel optimization algorithm, the “synchronous 4-points expected improvement”, EI(0,4). All the runs are performed simultaneously on the PACA Grid using the Scilab – ProActive Scheduler connector. The example reveals the sensitivity of the algorithm to the correlation lengths of the gaussian process ("rank1approx9d" problem, 100 random points chosen before the optimization).
![]()
Coordinator :
Call :
Statut :
SYSTEMATIC Working group :
Start date :
Finish date :
Duration :
Total amount :
Aid amount:
Members involved in the project :
![]()